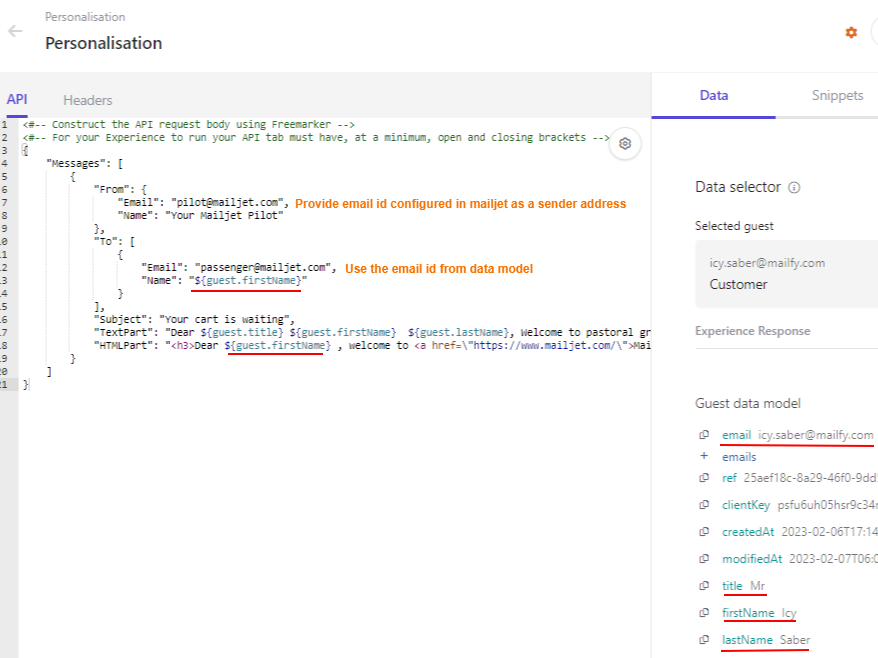
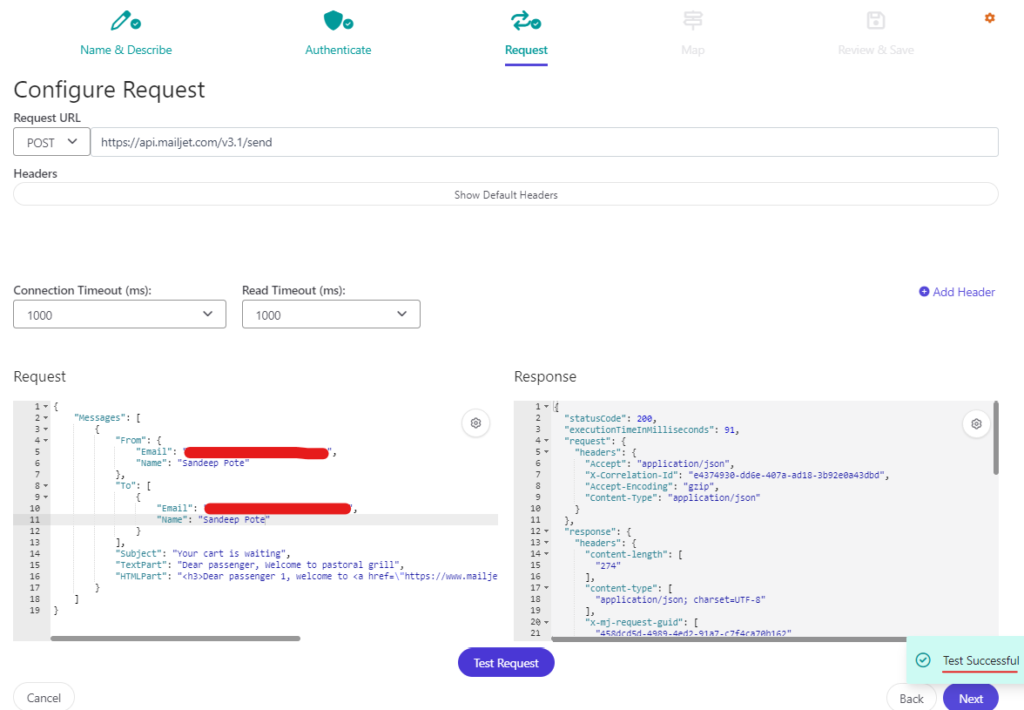
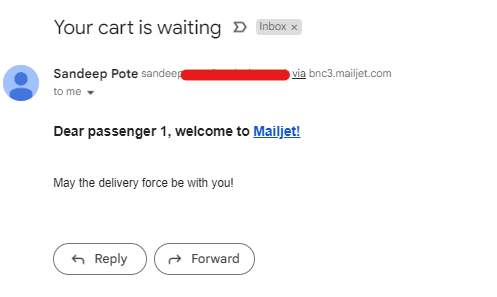
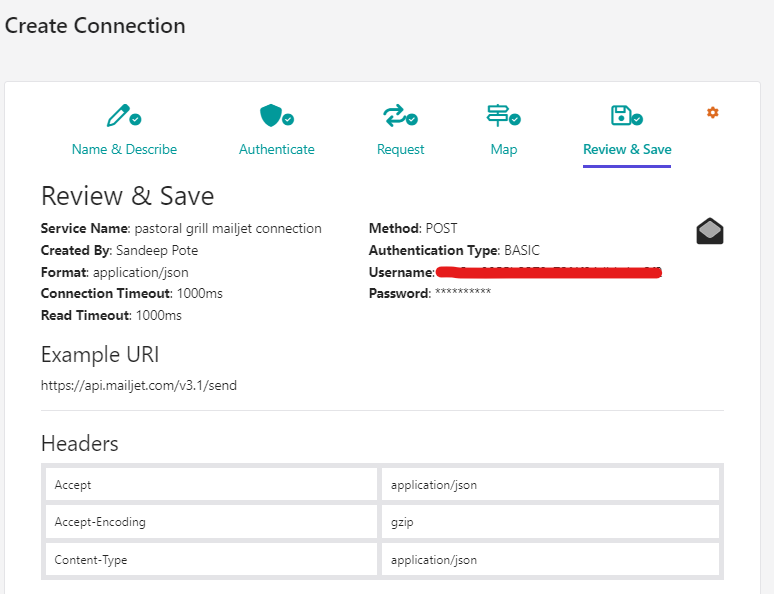
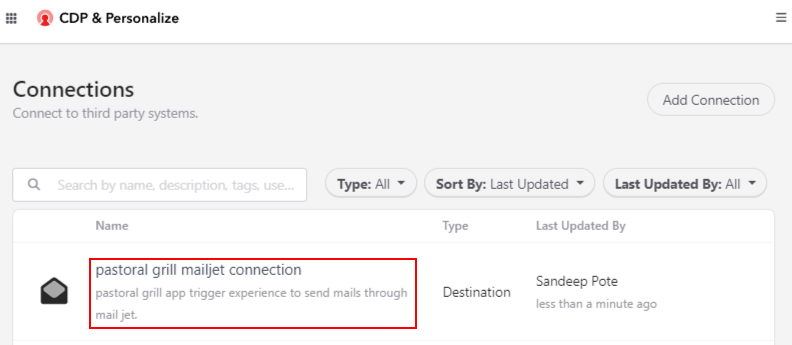
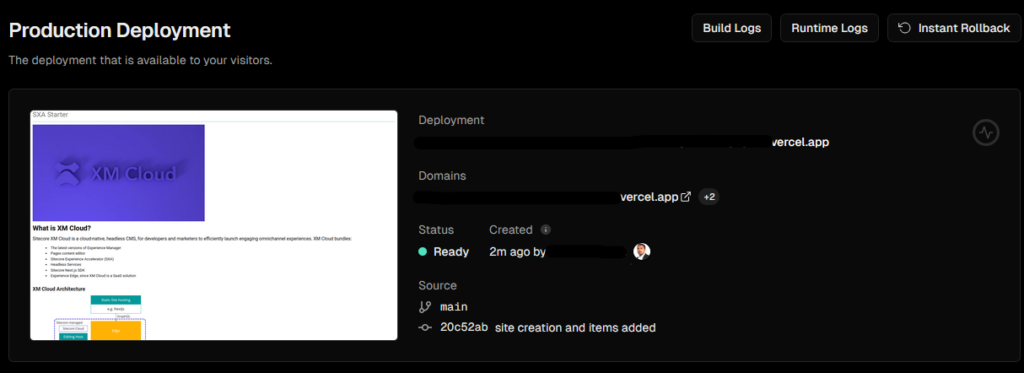
In this blog post we saw how to use Sitecore Grpahql Search query to filter the items.
But search query has issues with results getting same items with different version in Preview mode. This works fine for the published item (edge) as a single version of item is published.
I created a new version of the same item-

Using the same query
# Write your query or mutation here
query SearchQuery($pageSize: Int = 10, ) {
search(
where: {
AND: [
{
name: "_path"
value: "{B08684BB-3CB0-4DFE-A378-054E26ECC5AE}"
operator: CONTAINS
}
{ name: "ProductId", value: "bali-power-bank-3000mah" }
]
}
first: $pageSize
) {
total
results {
id
name
version
url {
path
}
... on Product{
productId{value}
productFeature{value}
}
}
}
}
See the output results in same item with versions available in Sitecore-
{
"data": {
"search": {
"total": 2,
"results": [
{
"id": "8716FE4AD58345589AB04369C39F5CC0",
"name": "bali-power-bank-3000mah",
"version": 2,
"url": {
"path": "/Data/Commerce-Data/Product-Data/bali-power-bank-3000mah"
},
"productId": {
"value": "bali-power-bank-3000mah"
},
"productFeature": {
"value": "UPDATE - official-camera - Product Feature. JIGA power bank is a high-quality battery pack, with all-day powerThe power bank can charge your phone at least 3-5 times,the perfect partner for gamers, camping and business trips."
}
},
{
"id": "8716FE4AD58345589AB04369C39F5CC0",
"name": "bali-power-bank-3000mah",
"version": 1,
"url": {
"path": "/Data/Commerce-Data/Product-Data/bali-power-bank-3000mah"
},
"productId": {
"value": "bali-power-bank-3000mah"
},
"productFeature": {
"value": "official-camera - Product Feature. JIGA power bank is a high-quality battery pack, with all-day powerThe power bank can charge your phone at least 3-5 times,the perfect partner for gamers, camping and business trips."
}
}
]
}
}
}See the highlighted fields in result. Same ID, multiple result set with different versions. Unfortunately, there is no option here to get the latest version. Sitecore has clarified this and raised a bug for same as of October 2025. this might be resolved in future. The related public reference number is DEVEX-2992.
How to solve this issue- This needs to be handled in headless app.
Headless app needs to filter this for each item and should pick only latest version from the result set for the same item.
function GetLatestVersion(products: ProductResult[])
{
if (products.length === 0)
{ return null; }
const latestVersions = Object.values( products.reduce<Record<string, ProductResult>>((acc, item) => {
const existing = acc[item.id];
if (!existing || item.version > existing.version)
{
acc[item.id] = item;
}
return acc;
},
{}));
return latestVersions;
}This should only provide the latest version of item.
![]()