Last Updated on February 1, 2025 by sandeeppote

All the commands for user account should run from root(i.e. supper user). Use SUDO command to get the privilege’s
See the current user details use id command
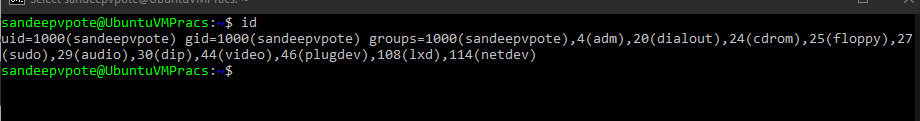
Check the name of the current user, use whoami command
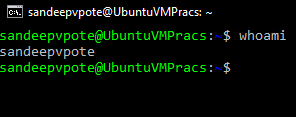
See users currently logged in to the system- use who command
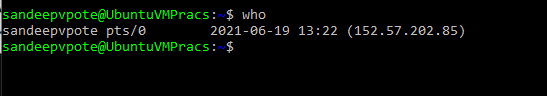
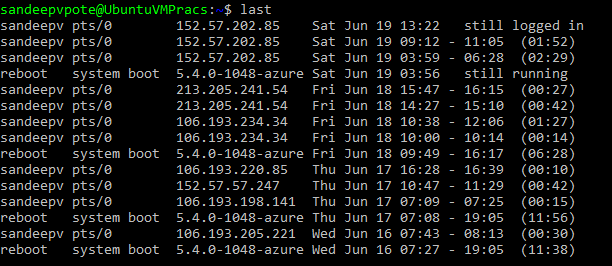
See the history of the users logged in to the system with the details system was rebooted, use last command-
Managing User
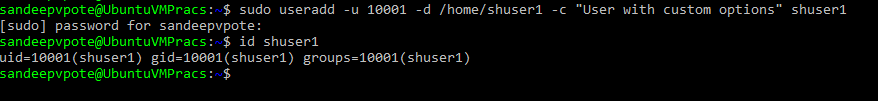
Adding a new user, use useradd command
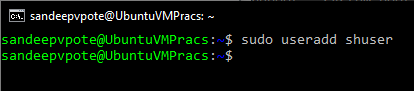
Check the newly created user, use grep command. User is created in /etc/passwd-
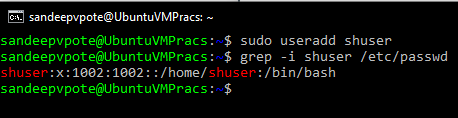
Following is the format of the user details in /etc/passwd-
shuser2:x:10001:10002:User with custom options:/home/shuser2:/bin/bash
USERNAME:PASSWORD:UID:GID:GECOS:HOMEDIR:SHELL
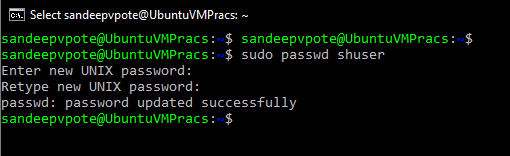
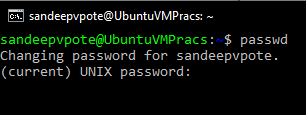
To set the password for newly created user, use passwd command
If the re-typed user password is wrong error is displayed
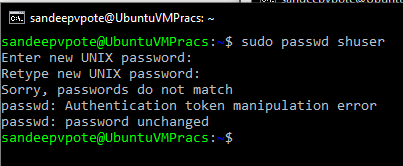
To change the current users password use passwd command without user name
Options whilst creating a user
| Options | Description |
| -c | set custom comments |
| -d | set custom home directory |
| -e | set expiry date |
| -g | set specific GID |
| -G | create user with multiple secondary group |
| -s | specify login shells |
| -u | specify UID |
Check the password of the user which is hashed is kept in /etc/shadow folder
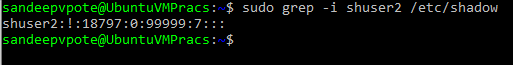
USERNAME:PASSWORD:LASTCHANGE:MINAGE:MAXAGE:WARN:INACTIVE:EXPDATE
MinAge– Minimum number of days user will have to wait to change the password
MaxAge– Maximum number of days user will have to change the password
EXPDate– if empty will never have to change the password
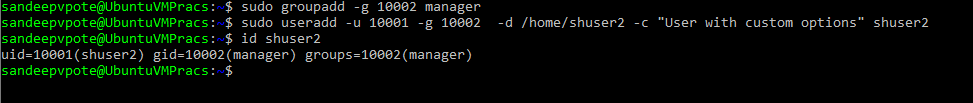
Add the user group using groupadd command and use -g option whilst creating user to assign user to newly created group
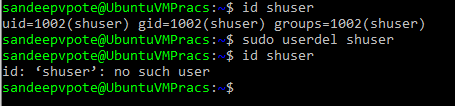
Deleting the user
To delete user use userdel command
Deleting the user group
To delete user group use groupdel command. If the user is assigned to the group it won’t allow to delete the group

Check the group of the user
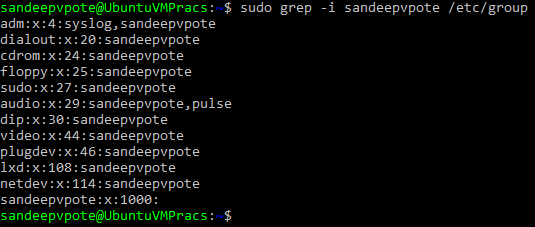
Following is the representation of the group detials-
NAME:PASSWORD:GID:MEMBERS





0 Comments
1 Pingback